Treatments and Technologies at the Brain Tumor Center at The Jewish Hospital – Mercy Health
Each patient’s treatment depends on the type, size and location of the tumor, so the Brain Tumor Center's specialists meet at a bi-weekly Tumor Board Conference to discuss complex cases, review treatment options and create a treatment plan for each individual patient.
For more information, please call (855) 823-1537.
Airo® Mobile Intraoperative CT Scanner
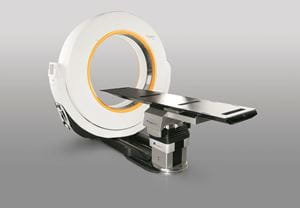 | This small but powerful mobile CT scanner provides high-resolution images in real time, giving surgeons a clear view of the patient’s anatomy during brain tumor surgery. The technology helps surgeons perform minimally invasive approaches and procedures and enables them to confirm that the tumor has been completely removed before the surgery is completed and no fragment is left behind. |
Awake Craniotomy
A craniotomy is a procedure in which neurosurgeons remove part of the skull. In some delicate procedures, this is done while the patient is awake so that the surgeon can use brain-mapping techniques to avoid critical functional areas, such as speech or arm movement. The patient performs tasks, such as reading, while the exposed brain is stimulated. The patient feels no pain.Chemotherapy: Intrathecal
Intrathecal chemotherapy involves the delivery of chemotherapy drugs into the brain or spinal fluid through a catheter or port. This treatment is appropriate for patients whose cancer cells have metastasized into the brain or spinal fluid.Chemotherapy: Systemic
The Brain Tumor Center offers the complete spectrum of systemic chemotherapy for patients with primary brain tumors or cancers that have metastasized to the brain from other parts of the body. Treatments include targeted therapies such as Avastin. Chemotherapy is often prescribed as a treatment in addition to surgery and/or radiosurgery.Continuous EEG Monitoring
State-of-the-art electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring is available for continuous, 24-hour use for patients who are undergoing or have undergone the removal of a brain tumor. Continuous EEG is used to monitor for electrical seizures that occur during surgery or after surgery when the patient is recovering in the intensive care unit.Endoscopic Surgery
Endoscopic surgery is minimally invasive surgery in which surgeons make small, keyhole incisions in the skull, eyelid or nose, and use long slender instrumentation (endoscopes) to remove tumors located deep within the brain. Endoscopic surgery is often performed during skull base surgery, with tumors being removed through the nose.Gamma Knife® ICON Radiosurgery
| Gamma Knife uses precise, high-intensity gamma rays to treat lesions in virtually any location in the brain with ultra-high precision and minimal effect on healthy tissue. When a small tumor is being treated, a single dose of radiation is given in a single session using a rigid frame. When a large tumor is being treated, radiation is given in 5 treatments using a mask system. The ICON promises accuracy to .5 millimeters while delivering a radiation dose to healthy tissue that is two to five times lower than competing technologies. The ICON’s frameless “mask” option enables treatment of previously challenging tumors, including large lesions. |